Last Updated on February 27, 2025 by Editor
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a cornerstone of modern technology, influencing various aspects of our daily lives. Traditionally, AI systems have operated under a centralized framework, where data is collected, processed, and managed in a single, central location. In this model, a central authority holds the reins, overseeing data storage and decision-making processes. While this approach offers streamlined data management and control, it also raises concerns about data privacy, security, and the potential for monopolistic control.
In contrast, decentralized AI distributes data processing and decision-making across a network of nodes, eliminating the need for a central authority. This architecture leverages technologies such as blockchain, federated learning, and edge computing to create a more collaborative and transparent AI ecosystem. By processing data locally on devices or within localized networks, decentralized AI enhances data privacy and security, as sensitive information doesn’t need to be transmitted to a central server. Moreover, this model fosters innovation by allowing a diverse range of participants, including individuals and smaller organizations, to contribute to AI development without the barriers imposed by centralized control.
The shift towards decentralized AI is gaining momentum in today’s technological landscape for several compelling reasons:
- Data Privacy and Security: With increasing concerns over data breaches and misuse, decentralized AI offers a solution by keeping data on local devices, reducing the risk associated with centralized data storage.
- Democratization of AI: Decentralized frameworks lower the barriers to entry for AI development, enabling a broader spectrum of contributors to participate and innovate. This inclusivity leads to a more diverse and rich AI ecosystem.
- Resilience and Fault Tolerance: By distributing processing tasks across multiple nodes, decentralized AI systems are inherently more robust against failures. The absence of a single point of failure ensures continuous operation even if some nodes go offline.
- Transparency and Trust: Utilizing blockchain technology, decentralized AI systems can provide immutable records of data transactions and decision-making processes, enhancing transparency and building user trust.
This article delves into the multifaceted world of decentralized AI, examining its benefits, the challenges it faces, and the potential future directions it may take. By exploring these aspects, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of how decentralized AI is poised to reshape the technological landscape, offering solutions that are more secure, inclusive, and resilient.

Understanding Decentralized AI
What is Decentralized AI?
Decentralized Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to AI systems where data processing and decision-making occur across a distributed network, rather than being centralized in a single location. In traditional, centralized AI models, data is gathered and processed in one central server or data center. This centralization can lead to concerns about data privacy, security, and potential single points of failure. In contrast, decentralized AI distributes these tasks across multiple nodes or devices, enhancing security and resilience.
Key Principles of Decentralized AI:
- Data Sovereignty: Users maintain control over their data, as information is processed locally on their devices rather than being sent to a central server.
- Enhanced Security: Distributing data processing reduces the risk of large-scale data breaches, as there isn’t a single repository of information.
- Scalability: Decentralized systems can grow organically, adding more nodes as needed without the bottlenecks that centralized systems might face.
Differences from Traditional AI:
- Control: Centralized AI is managed by a single entity, giving it full control over the data and algorithms. Decentralized AI, however, operates on a peer-to-peer basis, distributing control across all participants.
- Data Ownership: In centralized systems, users often relinquish ownership of their data to the central entity. Decentralized AI allows users to retain ownership, as data doesn’t leave their personal devices.
- Accessibility: Decentralized AI can democratize access to AI technologies, enabling individuals and smaller organizations to participate without needing vast resources.

Core Technologies Enabling Decentralized AI:
- Blockchain: Provides a secure and transparent ledger system, ensuring data integrity and trustworthiness without relying on a central authority.
- Federated Learning: Allows machine learning models to be trained across multiple devices holding local data samples, without exchanging the data itself. This approach enhances privacy and reduces data transfer requirements.
- Edge Computing: Involves processing data at the edge of the network, closer to the data source. This reduces latency and bandwidth use, enabling real-time processing and decision-making.
Ultimate AI Startup Guide: From Idea to Successful Venture
How Decentralized AI Works
Decentralized AI integrates several technologies to create a cohesive system where data processing and intelligence are distributed across various nodes.
Technology Stack:
- Blockchain for Transparency:
- Immutable Records: Blockchain maintains unchangeable records of all transactions and data exchanges, ensuring transparency and trust.
- Smart Contracts: These are self-executing contracts with the terms directly embedded in code, automating processes and reducing the need for intermediaries.
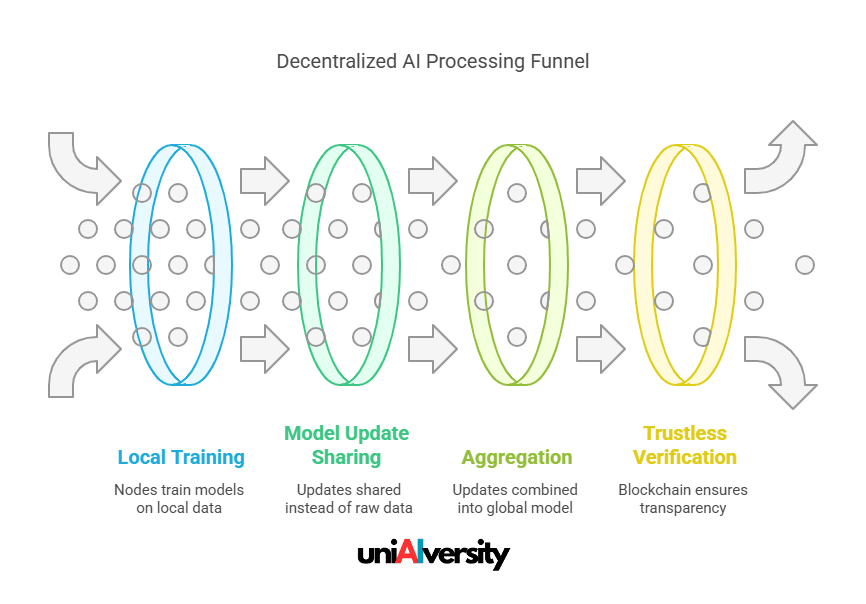
- Federated Learning for Privacy:
- Local Training: Models are trained on local devices using local data, and only the model updates (not the data) are shared with a central server for aggregation.
- Privacy Preservation: Since raw data remains on local devices, the risk of exposing sensitive information is minimized.
- Edge Computing for Efficiency:
- Proximity Processing: Data is processed near its source, reducing the time and resources needed to send data back and forth to central servers.
- Real-Time Analytics: This setup is ideal for applications requiring immediate responses, such as autonomous vehicles or IoT devices.

Data Processing Mechanisms:
- Local Training: Each node (e.g., a smartphone or IoT device) trains the AI model using its own data.
- Model Update Sharing: Instead of sharing raw data, nodes send their model updates to a central aggregator or use peer-to-peer sharing, depending on the system design.
- Aggregation: The received updates are combined to form an improved global model, which is then redistributed to all nodes.
- Trustless AI Models: By leveraging blockchain, decentralized AI systems can operate without requiring nodes to trust each other. The blockchain ensures that all transactions and data exchanges are transparent and verifiable.
This collaborative approach ensures that AI models improve over time while preserving data privacy and enhancing system resilience.
Opportunities and Benefits of Decentralized AI
Enhanced Privacy and Security
In today’s digital landscape, safeguarding personal data is paramount. Decentralized Artificial Intelligence (AI) addresses this concern by minimizing the risks associated with centralized data storage. By processing information across a distributed network, decentralized AI ensures that sensitive data remains on local devices, reducing the potential for large-scale breaches.
Techniques Enhancing Privacy in Decentralized AI:
- Federated Learning: This approach allows AI models to be trained on data located on individual devices. Instead of sending raw data to a central server, only the model updates are shared, preserving user privacy.
- Homomorphic Encryption: This encryption method enables computations on encrypted data without decrypting it, ensuring that sensitive information remains confidential throughout the processing.
- Differential Privacy: By introducing statistical noise into datasets, differential privacy ensures that individual data points cannot be identified, even during analysis.

Industry Applications:
- Healthcare: Decentralized AI allows medical institutions to collaboratively train AI models on patient data without sharing the actual data, enhancing patient confidentiality.
- Finance: Financial organizations can utilize decentralized AI to detect fraudulent activities by analyzing transaction patterns across institutions without exposing individual customer data.
- Cybersecurity: Implementing federated learning in cybersecurity enables the development of threat detection models based on data from multiple sources, all while keeping sensitive information secure.
Democratizing AI Access
Traditionally, AI development has been dominated by large corporations with substantial resources. Decentralized AI is shifting this paradigm by making advanced AI tools and platforms accessible to startups, researchers, and individual developers.
Key Factors Contributing to Democratization:
- Open-Source Platforms: The rise of open-source AI frameworks allows developers worldwide to collaborate, share innovations, and build upon existing technologies without hefty licensing fees.
- Decentralized Compute Networks: Platforms like NodeGo enable users to share and monetize unused computing power, providing affordable resources for AI development.

Economic Benefits:
- Lower Barriers to Entry: By reducing the cost associated with AI development, decentralized AI encourages innovation from a diverse pool of contributors, leading to a more vibrant and competitive market.
- Incentivized Participation: Decentralized AI platforms often reward users, data providers, and model trainers, ensuring that those who contribute to the ecosystem benefit economically.
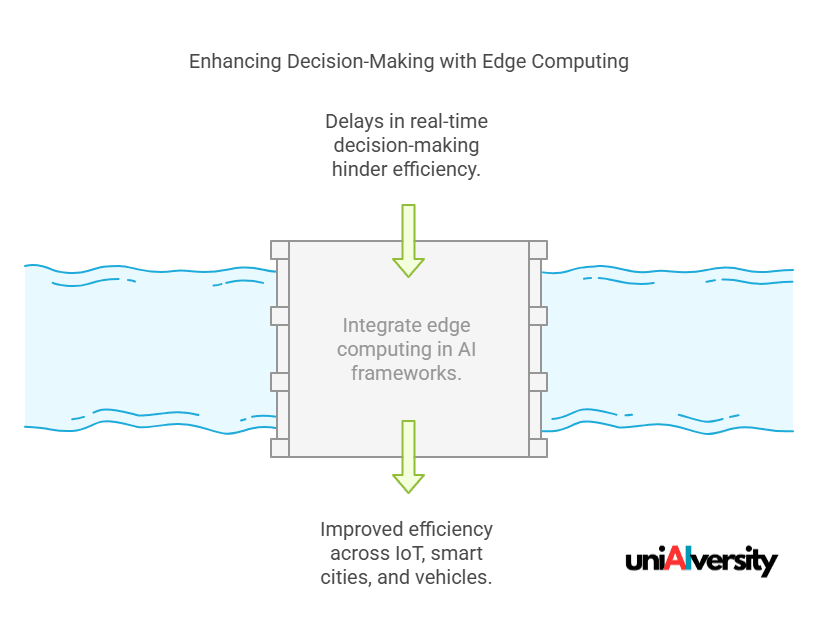
Real-Time Decision-Making and Efficiency
The integration of edge computing in decentralized AI frameworks significantly enhances the speed and efficiency of data processing.
Advantages of Edge Computing:
- Reduced Latency: Processing data closer to its source eliminates the delays associated with transmitting information to centralized servers, enabling real-time responses.
- Bandwidth Optimization: Local data processing decreases the need for extensive data transfers, conserving network bandwidth.
Impact on Applications:
- Internet of Things (IoT): Devices such as smart thermostats and wearable health monitors can make instantaneous decisions based on real-time data analysis.
- Smart Cities: Decentralized AI facilitates efficient traffic management, energy distribution, and public safety measures by analyzing data locally.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars rely on rapid data processing to navigate safely; decentralized AI ensures they can process environmental data in real-time.
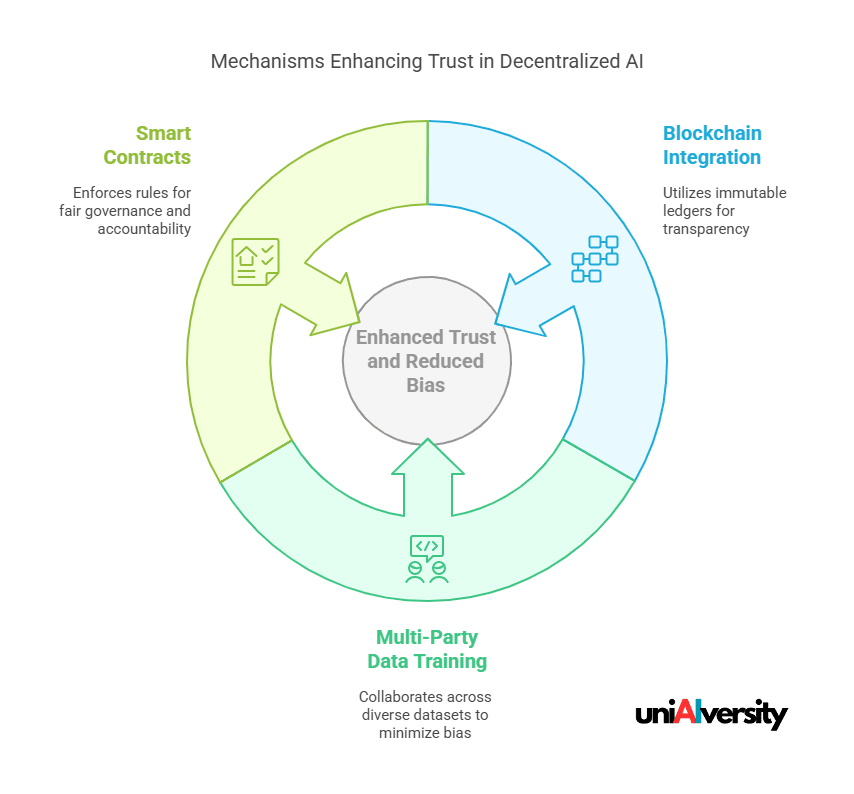
Transparency, Trust, and Bias Reduction
Building user trust is essential for the widespread adoption of AI technologies. Decentralized AI enhances transparency and reduces biases through several mechanisms.
Enhancing Trust through Technology:
- Blockchain Integration: Utilizing blockchain’s immutable ledger, decentralized AI systems can provide verifiable records of data sources and decision-making processes, ensuring transparency.
- Multi-Party Data Training: Collaborative model training across diverse datasets helps in minimizing biases, leading to more equitable AI outcomes.
- Smart Contracts: These self-executing contracts enforce agreed-upon rules within decentralized AI systems, ensuring fair governance and accountability.
By addressing privacy concerns, promoting inclusivity, enhancing efficiency, and ensuring transparency, decentralized AI stands poised to revolutionize various industries, fostering a more secure and equitable technological landscape.
Challenges Hindering Decentralized AI Adoption
While Decentralized Artificial Intelligence (AI) offers numerous benefits, its adoption faces several significant challenges that need to be addressed to realize its full potential.
Scalability and Performance Issues
Decentralized AI systems distribute data processing across multiple nodes, which can lead to computational limitations. Each node may have restricted processing power, causing delays in data analysis and decision-making. Additionally, as the network grows, ensuring efficient communication between nodes becomes increasingly complex, potentially leading to latency and reduced performance.
Improving Performance While Maintaining Decentralization:
- Optimized Algorithms: Developing algorithms tailored for decentralized environments can enhance efficiency.
- Edge Computing Integration: Processing data closer to its source reduces the load on central nodes and minimizes latency.
- Resource Allocation Strategies: Implementing dynamic resource management can ensure balanced workloads across the network.
Interoperability and Standardization
The absence of unified protocols in decentralized AI systems poses challenges for seamless integration and communication between diverse platforms. This lack of standardization can lead to compatibility issues, hindering collaboration and data sharing across different systems.
Need for Open Standards and Collaboration:
- Developing Common Protocols: Establishing universal communication standards can facilitate interoperability.
- Collaborative Frameworks: Encouraging partnerships between organizations can lead to the creation of cohesive ecosystems.
- Regulatory Support: Governments and international bodies can play a pivotal role in promoting standardization efforts.
Ethical and Accountability Concerns
Operating without centralized oversight raises questions about regulating AI models and ensuring ethical behavior. Decentralized systems may lack clear accountability, making it difficult to address biases or malicious activities that could arise within the network.
Shadow AI: The Hidden Threat of Unregulated AI in the Workplace
Addressing Ethical Challenges:
- Transparent Frameworks: Implementing clear guidelines can help in monitoring AI behavior.
- Decentralized Oversight Mechanisms: Establishing community-driven oversight can enhance accountability.
- Ethics Training: Educating developers and users about ethical considerations is crucial for responsible AI deployment.
Regulatory and Legal Uncertainties
The evolving nature of decentralized AI often outpaces existing legal frameworks, leading to ambiguities in governance. Ensuring compliance with global data protection laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), becomes complex when data is processed across multiple jurisdictions.
Navigating Legal Complexities:
- Adaptive Regulations: Policymakers need to craft laws that accommodate the unique aspects of decentralized AI.
- International Cooperation: Harmonizing regulations across borders can provide clarity and facilitate broader adoption.
- Legal Frameworks: Establishing clear legal guidelines can help in navigating the complexities of decentralized AI.
Security Risks and Cyber Threats
Decentralized AI systems, while offering enhanced privacy, are not immune to security vulnerabilities. The distributed nature can make it challenging to implement consistent security measures, potentially exposing the network to cyberattacks.
Mitigating Security Threats:
- Blockchain Integration: Utilizing blockchain technology can enhance data integrity and security.
- Advanced Encryption Techniques: Implementing robust encryption methods can protect data across the network.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting frequent assessments can identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative effort from researchers, policymakers, and industry stakeholders to develop solutions that balance innovation with ethical and legal responsibilities.
Real-World Applications of Decentralized AI
Decentralized Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming various industries by enhancing data security, operational efficiency, and decision-making processes. By distributing AI computations across multiple nodes, decentralized AI ensures data privacy and reduces reliance on centralized systems. Below are key sectors benefiting from this innovative approach:
Healthcare
Secure Medical Research and Patient Data Privacy
In the healthcare sector, protecting patient information is paramount. Decentralized AI enables medical institutions to collaborate on research without sharing sensitive data. By processing information locally and sharing only the necessary insights, patient privacy is maintained while advancing medical research. This approach fosters innovation without compromising confidentiality.
Federated Learning in Medical AI Applications
Federated learning allows AI models to be trained on data from multiple healthcare providers without centralizing the data. Each institution trains the model locally, and only the model updates are aggregated. This method enhances the accuracy of AI applications in diagnostics and treatment recommendations while ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
Financial Services
Fraud Detection with Blockchain-Integrated AI
Financial institutions are leveraging decentralized AI combined with blockchain technology to combat fraud. By analyzing transaction data across a distributed ledger, anomalies can be detected in real-time, enhancing the security of financial transactions. This integration ensures data integrity and provides a transparent audit trail, making fraudulent activities easier to identify and prevent.
Decentralized AI for Automated Trading and Credit Scoring
Decentralized AI is revolutionizing automated trading by enabling algorithms to operate across distributed networks, reducing latency, and improving decision-making speed. In credit scoring, AI models assess creditworthiness by analyzing diverse data sources without exposing personal information, leading to more accurate and fair lending decisions.
Smart Cities and IoT
Optimizing Energy Grids and Traffic Management
Smart cities utilize decentralized AI to enhance infrastructure efficiency. By processing data from IoT devices locally, energy consumption patterns are analyzed in real-time, allowing for dynamic adjustments in energy distribution. Similarly, traffic data is processed at the edge, enabling immediate responses to congestion and improving overall traffic flow.
Real-Time Decision-Making for Autonomous Systems
Autonomous vehicles and drones rely on decentralized AI for real-time data processing. By analyzing environmental data locally, these systems can make instantaneous decisions, enhancing safety and operational efficiency. This approach reduces dependence on constant connectivity to central servers, allowing for more robust autonomous operations.
Supply Chain and Logistics
AI-Driven Transparency in Tracking Goods
Decentralized AI enhances supply chain transparency by enabling real-time tracking of goods. By integrating AI with blockchain technology, each step of a product’s journey is recorded on a distributed ledger, providing an immutable and transparent history. This visibility helps in verifying the authenticity of products and ensures compliance with regulatory standards.
Smart Contracts Automating Logistics Processes
In logistics, smart contracts—self-executing agreements coded on a blockchain—automate processes such as inventory management, shipment scheduling, and payment settlements. Decentralized AI monitors these contracts, ensuring they execute based on real-time data and predefined conditions, thereby reducing manual intervention and increasing operational efficiency.
The integration of decentralized AI across these sectors not only enhances operational capabilities but also addresses critical concerns related to data privacy, security, and efficiency. As technology continues to evolve, the adoption of decentralized AI is poised to become increasingly prevalent, driving innovation and transformation across industries.
Future Trends in Decentralized AI
As Decentralized Artificial Intelligence (AI) continues to evolve, several emerging trends are poised to shape its trajectory, integrating cutting-edge technologies and innovative approaches to enhance functionality, privacy, and accessibility.
Integration with Emerging Technologies
Web3, Metaverse Applications, and Quantum AI Convergence
The convergence of decentralized AI with Web3, the Metaverse, and quantum computing is forging new pathways for technological advancement.
- Web3 and Decentralized AI: Web3 aims to create a decentralized internet, reducing reliance on centralized entities. Integrating decentralized AI into Web3 enhances data privacy and user autonomy, enabling intelligent applications that operate on decentralized networks.
- Metaverse Applications: In the Metaverse—a collective virtual shared space—decentralized AI facilitates real-time, personalized user experiences. By processing data locally or on distributed networks, it ensures seamless interactions within virtual environments.
- Quantum AI Convergence: Quantum computing offers unprecedented processing capabilities, accelerating complex AI computations. The fusion of quantum computing with decentralized AI can lead to more efficient algorithms and enhanced data security, addressing challenges previously deemed insurmountable.
Evolving Privacy-Preserving Techniques
Advances in Cryptographic AI Security Models
Protecting user data remains a cornerstone of decentralized AI development. Emerging cryptographic techniques are enhancing privacy and security:
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs): ZKPs allow one party to prove to another that a statement is true without revealing any information beyond the validity of the statement itself. In AI, ZKPs can verify computations without exposing underlying data, bolstering trust in AI systems.
- Secure Multi-Party Computation (MPC): MPC enables multiple parties to collaboratively compute a function over their inputs while keeping those inputs private. This technique is vital for training AI models on data from different sources without compromising confidentiality.
These advancements are crucial for sectors like healthcare and finance, where data sensitivity is paramount.
Regulatory Sandboxes for Innovation
Governments Creating Controlled Environments for AI Innovation and Compliance
As decentralized AI technologies advance, regulatory frameworks must adapt to ensure ethical deployment and compliance:
- Regulatory Sandboxes: These are controlled environments where companies can test innovative AI solutions under regulatory supervision. Sandboxes allow for experimentation with decentralized AI applications while ensuring adherence to legal and ethical standards.
- Policy Development: Collaborative efforts between policymakers, technologists, and ethicists are essential to create guidelines that foster innovation without compromising public trust or safety.
Such initiatives encourage responsible AI development and provide clarity for businesses navigating the complex regulatory landscape.
Decentralized AI and AI-as-a-Service (AIaaS)
AI Marketplaces Leveraging Decentralized Infrastructures
The rise of AI-as-a-Service (AIaaS) platforms is democratizing access to AI technologies:
- Decentralized Marketplaces: These platforms allow developers to share and monetize AI models on a decentralized network, reducing barriers to entry and fostering innovation.
- Interoperability and Standardization: To maximize the potential of decentralized AIaaS, establishing open standards is crucial. This ensures seamless integration and collaboration across diverse systems and applications.
By leveraging decentralized infrastructures, AIaaS platforms can offer more secure, transparent, and cost-effective solutions to a global audience.
In short, the future of decentralized AI is being shaped by its integration with emerging technologies, advancements in privacy-preserving methods, supportive regulatory frameworks, and the proliferation of decentralized AI services. These trends collectively contribute to a more secure, efficient, and inclusive AI ecosystem.
Global Impact and Societal Implications
The advent of Decentralized Artificial Intelligence (AI) is poised to bring about significant transformations in global economies and societal structures. By distributing AI capabilities across networks, decentralized AI offers a paradigm shift with profound economic and ethical consequences.
Economic and Employment Shifts
Reshaping AI-Driven Economies
Decentralized AI is set to redefine economic landscapes by democratizing access to AI technologies. This shift enables a broader spectrum of participants, including startups and individual developers, to contribute to AI innovation without the need for substantial capital investment. Such inclusivity fosters a more competitive market, potentially leading to increased productivity and economic growth. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) highlights that AI-related innovations are associated with faster employment and revenue growth, as well as higher output per worker.
Impact on Job Markets and AI Startups
The integration of decentralized AI into various industries is anticipated to influence employment patterns significantly. While automation may streamline certain tasks, leading to the displacement of some roles, it also creates opportunities for new job categories centered around AI development, maintenance, and oversight. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a 10.5% growth in jobs within the professional, scientific, and technical services sector from 2023 to 2033, driven by the increasing complexity of digital systems requiring skilled human oversight.
Moreover, decentralized AI lowers barriers to entry for AI startups by reducing reliance on centralized infrastructure. This accessibility allows emerging companies to innovate and compete with established tech giants, fostering a diverse and dynamic AI ecosystem. For instance, initiatives like Sahara AI reward users, data sources, and AI trainers on its decentralized blockchain platform, promoting transparency and equitable distribution of benefits.
Ethical AI for a Fairer World
Promoting Inclusivity and Diversity
Decentralized AI has the potential to enhance inclusivity and diversity within technological development. By distributing control and access, it empowers underrepresented groups to participate actively in AI innovation. This collaborative approach can lead to AI systems that better reflect diverse perspectives, reducing biases and promoting fairness. However, challenges persist; for example, recent shifts in corporate policies have seen companies like Google scaling back diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) initiatives, sparking debates about the commitment to inclusivity in AI development.
Ensuring Responsible AI Use Across Global Communities
The decentralized nature of this technology necessitates robust frameworks to ensure ethical standards are upheld universally. Collaborative efforts between governments, industry stakeholders, and civil society are essential to establish guidelines that promote transparency, accountability, and fairness in AI applications. The IMF emphasizes the need for policies that balance AI’s potential with ethical considerations to ensure its benefits are equitably distributed.
Decentralized AI offers promising avenues for economic advancement and societal inclusivity. By proactively addressing the accompanying challenges, global communities can harness its potential to foster a more equitable and prosperous future.
Conclusion
Decentralized Artificial Intelligence (AI) stands at the forefront of technological evolution, offering transformative potential across various sectors. By distributing AI capabilities across networks, it enhances data privacy, democratizes access to advanced technologies, and fosters innovation beyond the confines of centralized entities. This paradigm shift not only empowers individuals and smaller organizations but also paves the way for more resilient and transparent AI systems.
However, the journey toward a fully decentralized AI ecosystem is not without challenges. Scalability issues, interoperability hurdles, ethical considerations, and regulatory uncertainties present significant obstacles that must be addressed to ensure a sustainable future for decentralized AI. Overcoming these challenges requires a concerted effort to develop robust frameworks, establish open standards, and create governance models that balance innovation with ethical responsibility.
Collaboration is paramount in this endeavor. Businesses, developers, policymakers, and the broader community must unite to shape the trajectory of decentralized AI. By fostering open-source initiatives, sharing knowledge, and engaging in transparent dialogue, stakeholders can collectively build an AI landscape that is inclusive, secure, and aligned with societal values. Such collaborative efforts will not only accelerate technological advancements but also ensure that the benefits of AI are equitably distributed across global communities.
In essence, the future of decentralized AI hinges on our collective commitment to innovation, ethical integrity, and cooperative action. Embracing these principles will enable us to harness the full potential of decentralized AI, driving progress and prosperity in an increasingly interconnected world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Decentralized AI
Sources and More Reads
- The Promise of Decentralized AI: Opportunities and Challenges
- The Future of Artificial Intelligence | IBM
- A Critical & Systematic Understanding the Decentralized AI Paradigm
- Decentralized AI: Transforming the Future of Technology with Blockchain and AI Integration – Blaize
- Decentralized AI Transforming Industry In 2025 | Interexy
- Decentralized AI Demystified: A Beginner’s Guide
- What is Decentralized AI?
- AI and Privacy: Ensuring Equilibrium between Technological Advancements and Consumer Protections | ProfileTree
- Frontiers | Advancing cybersecurity and privacy with artificial intelligence: current trends and future research directions
- The Intersection of AI and Web3: Unraveling the Impact on the Decentralized Future
- The Convergence of Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain: The State of Play and the Road Ahead
- Decentralizing AI—Big Dreams, Bigger Hype?
- III. Artificial intelligence and the economy: implications for central banks
- The Rise of Decentralized AI: Challenging Tech Monopoly
- How to Overcome Challenges in Decentralized AI: All-in-One Guide
- Use of Artificial Intelligence in Terms of Open Innovation Process and Management
- AI Watch: Global regulatory tracker – United States | White & Case LLP
- The Economic Impacts and the Regulation of AI: A Review of the Academic Literature and Policy Actions
- What Decentralized AI Means for You
- AI Crypto Infrastructure: Trends, Projects, and Opportunities | Shift Markets
- Ethereum and AI: Building Decentralized AI Applications on the Ethereum Blockchain
- The Future of Decentralized AI: Trends and Predictions
- Future Directions in AI Research: Trends and Predictions
- Integrating AI and Blockchain for Decentralized ApplicationsIntegrating AI and Blockchain for Decentralized Applications
- The Rise of AI: Exploring Cutting-Edge Technologies and Their Impact on Society
- The Intersection of AI and Emerging Markets: Opportunities and Challenges
- Dissecting the Paradox of Progress: The Socioeconomic Implications of Artificial Intelligence
- Decentralized AI: Transforming Technology with Blockchain
- Decentralized AI: Pros and Cons
- Decentralized AI: Answer Future Trends
- Decentralized AI in 2025: Transforming Technology for an Inclusive Future
- Decentralized AI: Answer Trends in AI 2025 Cat Ai
- How to Overcome Challenges in Decentralized AI: All-in-One Guide
- Decentralized AI: Ultimate Guide for Beginners
- Decentralized AI Transforming Industry In 2025
- Next Big Technology Trend 2025: Decentralized AI Platforms
- Crypto Trends 2025: AI Integration and Decentralized Finance
- The Rise of Decentralized AI: Challenging Tech Monopoly
- Top Decentralized AI Projects of 2025 Amid OpenAI Copyright Concerns
- AI/ML Trends 2025
- Challenges in Decentralizing AI
- Will the 2025 AI supercycle lead to decentralization?
- Decentralized AI Demystified: A Beginner’s Guide
- Blockchain Predictions and Trends to Watch in 2025
- Decentralized Roundtable 2 Aug 20 2024
- Web3 in 2025: Decentralized Platforms
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and AI: Innovations at the Intersection of Blockchain and Artificial Intelligence